Introduction
In this article, we will discuss the process of establishing a secure and automated system for secret management for the environment.
Additionally, we will cover how to implement centralized log monitoring enhancing observability and operational efficiency.
-
Secret Management:
Utilizes Azure Key Vault to securely manage and store sensitive information such as credentials, certificates, and secrets. This guarantees consistent and secure access across all applications and services. -
Centralized Application Log Management:
Implements a centralized logging system using Azure Log Analytics and Application Insights to collect and analyze logs from all applications. This setup allows for effective performance monitoring, issue troubleshooting, and operational insight maintenance across the environment. -
CI/CD flow:
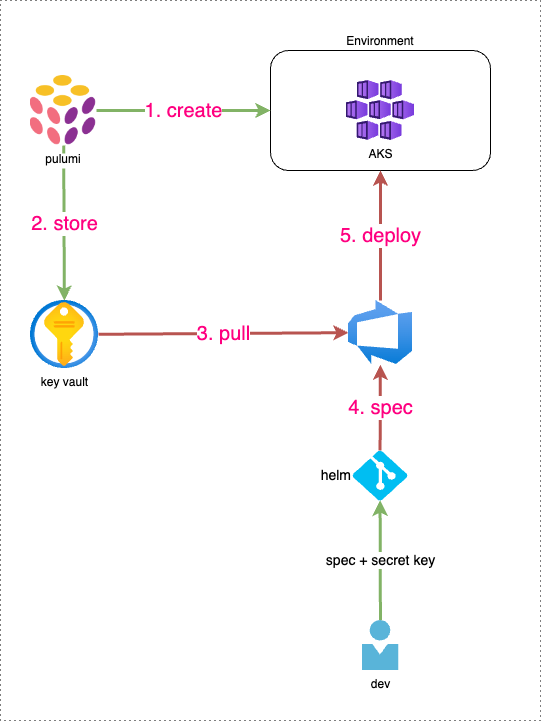
Illustration of the software CI/CD flow
- The purpose of this CI/CD flow is to ensure that environment secrets, especially for production, are automatically generated by Pulumi and stored securely in Azure Key Vault.
- When developers need to deploy an application, they only need to specify the secret name in the deployment spec.
- During the deployment process, the CI/CD pipeline will automatically replace the secret name with the actual secret from Key Vault.
- This approach guarantees that sensitive production secrets remain secure and are not exposed to the team members.
Table of Contents
Open Table of Contents
Configuration
Before we start coding, it’s important to define our configuration settings. This involves specifying resource names and subnet address spaces that we’ll use throughout the project.
Resource Groups
We categorize our resources into different Azure resource groups for better organization and management:
| Resource Group | Description |
|---|---|
| Shared Resource Group | Where our Key Vault and logging components reside. |
| Hub VNet Resource Group | Contains our main VNet hub. |
| AKS VNet Resource Group | Contains resources specific to the AKS cluster. |
| CloudPC VNet Resource Group | For resources related to virtual desktops or cloud PCs. |
Allocated Subnets
Again, this is the subnet Ip address spaces that we have defined in the previous post.
| VNet Name | Subnet Name | Address Prefix | Total | Usable |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Hub VNet | 1.1 Firewall Subnet | 192.168.30.0/26 | 64 | 59 |
| 1.2 Firewall Management Subnet | 192.168.30.64/26 | 54 | 59 | |
| 1.3 General Subnet | 192.168.30.128/27 | 32 | 27 | |
| 2. AKS VNet | 2.1 AKS Subnet | 192.168.31.0/24 | 256 | 251 |
| 3. CloudPC VNet | 3.1 CloudPC Subnet | 192.168.32.0/25 | 128 | 123 |
| 3.2 DevOps Subnet | 192.168.32.128/27 | 32 | 27 |
The configuration file
Here is the config.ts file will be used for all pulumi our projects:
View code:
export const azGroups = {
//The name of Shared resource group
shared: '01-shared',
//The name of Hub VNet resource group
hub: '02-hub',
//The name of AKS VNet resource group
aks: '03-aks',
//The name of CloudPC VNet resource group
cloudPC: '04-cloudPC',
};
//The subnet IP address spaces
export const subnetSpaces = {
firewall: '192.168.30.0/26',
firewallManage: '192.168.30.64/26',
general: '192.168.30.128/27',
aks: '192.168.31.0/24',
cloudPC: '192.168.32.0/25',
devOps: '192.168.32.128/27',
};
Note: Adding a number as a prefix to the Azure resource group names helps keep them sorted in sequence, making them easier to find and navigate.
The Common Project
To promote code reusability and maintainability, we create a common project named az-commons.
This library contains utilities and helper functions that we’ll use across all our Pulumi projects.
The azEnv Module
This module provides functions to retrieve Azure environment configurations:
- Tenant ID: Identifies the Azure Active Directory (EntraID) tenant.
- Subscription ID: Identifies the Azure subscription where resources will be deployed.
- Current Principal: The object ID of the user or service principal executing the scripts.
- Region Code: The Azure region.
View code:
import * as azure from '@pulumi/azure-native';
import * as pulumi from '@pulumi/pulumi';
// Parse the Pulumi configuration from the environment variable
const env = JSON.parse(process.env.PULUMI_CONFIG ?? '{}');
// Retrieve the current Azure client configuration
const config = azure.authorization.getClientConfigOutput();
// Export the tenant ID from the Azure client configuration
export const tenantId = config.tenantId;
// Export the subscription ID from the Azure client configuration
export const subscriptionId = config.subscriptionId;
// Export the object ID of the current principal (user or service principal)
export const currentPrincipal = config.objectId;
// Export the current Azure region code, defaulting to "SoutheastAsia" if not set
export const currentRegionCode = env['azure-native:config:location']!;
//Print and Check
pulumi.all([subscriptionId, tenantId]).apply(([s, t]) => {
console.log(`Azure Environment:`, {
tenantId: t,
subscriptionId: s,
currentRegionCode,
});
});
The naming Module
This module helps generate resource names with a consistent prefix based on the Pulumi stack name:
getGroupName: Prepends the stack name to a resource group name.getName: uses to format the name with convention {stack}-nameWithoutNumber-{suffix} and remove the numbers from the name.
View code:
The stackEnv Module
This module provides functions to retrieve Pulumi stack environment configurations:
isDryRun: Indicates whether the current execution is a dry run (preview) or an actual deployment.- Organization: The Pulumi organization name.
- Project Name: The name of the Pulumi project.
- Stack: The name of the Pulumi stack.
- StackReference: This helper function ensures that a project correctly references stacks within the same organization and environment.
For example, the
devstack of projectaz-02-hub-vnetwill reference thedevstack of projectaz-01-shared. This mechanism prevents cross-environment resource referencing, ensuring that resources from different environments (e.g., dev and prod) are kept isolated and properly aligned within the intended environment.
View code:
import * as pulumi from '@pulumi/pulumi';
export const isDryRun = Boolean(process.env.PULUMI_NODEJS_DRY_RUN);
export const organization = process.env.PULUMI_NODEJS_ORGANIZATION!;
export const projectName =
process.env.PULUMI_NODEJS_PROJECT ?? pulumi.getProject().toLowerCase();
export const stack =
process.env.PULUMI_NODEJS_STACK ?? pulumi.getStack().toLowerCase();
/**Get stack reference for a project*/
export const StackReference = <TOutput>(
projectName: string
): pulumi.Output<TOutput> => {
const stackRef = new pulumi.StackReference(
`${organization}/${projectName}/${stack}`
);
return stackRef.outputs.apply(
(s) => s.default ?? s
) as pulumi.Output<TOutput>;
};
/**Get stack reference for current project*/
export const CurrentProjectReference = <TOutput>() =>
StackReference<TOutput>(projectName);
console.log('Pulumi Environments:', {
organization,
projectName,
stack,
isDryRun,
});
The Shared Project
Following the instructions from Day 01, we create a new project named az-01-shared.
This project will include the following components:
The Vault Module
Creating a Azure Key Vault is a secure storage solution for managing secrets, keys, and certificates. It helps safeguard cryptographic keys and secrets used by cloud applications and services.
-
Vault Options:
- enablePurgeProtection: This option enables purge protection for the Key Vault. When enabled, it prevents the permanent deletion of the vault and its contents for a specified retention period, even if a delete operation is performed. This is crucial for compliance and recovery scenarios.
- enabledForDiskEncryption: This setting allows the Key Vault to be used for Azure Disk Encryption. It is necessary for encrypting virtual machine disks, ensuring that data at rest is protected.
- softDeleteRetentionInDays: This specifies the number of days that deleted vault items (like keys, secrets, and certificates) are retained in a “soft deleted” state. During this period, they can be recovered. The minimum value is 7 days, and the maximum is 90 days.
- enableRbacAuthorization: This enables Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) for managing access to the Key Vault. It requires authentication through EntraID, allowing for more granular and secure access management.
-
Vault Roles Management: To implement the principle of least privilege, we create two EntraID groups:
- AZ ROL DEV-SHARED-VLT READONLY: For read-only access to the Key Vault.
- AZ ROL DEV-SHARED-VLT WRITE: For write access to the Key Vault.
View code:
import { currentPrincipal, tenantId } from '@az-commons';
import * as azure from '@pulumi/azure-native';
import * as ad from '@pulumi/azuread';
export default (
name: string,
{
//it should be 90 days or more in PRD
retentionInDays = 7,
rsGroup,
}: {
retentionInDays?: number;
rsGroup: azure.resources.ResourceGroup;
}
) => {
const vaultName = name;
const vault = new azure.keyvault.Vault(
vaultName,
{
resourceGroupName: rsGroup.name,
properties: {
//This must be enabled for VM Disk encryption
enablePurgeProtection: true,
enabledForDiskEncryption: true,
//soft delete min value is '7' and max is '90'
softDeleteRetentionInDays: retentionInDays,
//Must be authenticated with EntraID for accessing.
enableRbacAuthorization: true,
//enabledForDeployment: true,
tenantId,
sku: {
name: azure.keyvault.SkuName.Standard,
family: azure.keyvault.SkuFamily.A,
},
},
},
{ dependsOn: rsGroup }
);
/** As the key vault is requiring Rbac authentication.
* So We will create 2 EntraID groups for ReadOnly and Write access to this Key Vault
*/
const vaultReadOnlyGroup = new ad.Group(`${vaultName}-readOnly`, {
displayName: `AZ ROL ${vaultName.toUpperCase()} READONLY`,
securityEnabled: true,
//add current principal as an owner.
owners: [currentPrincipal],
});
const vaultWriteGroup = new ad.Group(`${vaultName}-write`, {
displayName: `AZ ROL ${vaultName.toUpperCase()} WRITE`,
securityEnabled: true,
//add current principal as an owner.
owners: [currentPrincipal],
//Add current member in to ensure the AzureDevOps principal has WRITE permission to Vault
members: [currentPrincipal],
});
/**
* These roles allow read access to the secrets in the Key Vault, including keys, certificates, and secrets.
* The role names and IDs are provided here for reference, but only the ID is used in the code.
* All roles are combined into a single Entra ID group in this implementation. However, you can split them
* into separate groups depending on your environment's requirements.
*
* To retrieve all available roles in Azure, you can use the following REST API:
* https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/role-based-access-control/role-assignments-list-rest
*/
//ReadOnly Roles
[
{
name: 'Key Vault Crypto Service Encryption User',
id: 'e147488a-f6f5-4113-8e2d-b22465e65bf6',
},
{
name: 'Key Vault Secrets User',
id: '4633458b-17de-408a-b874-0445c86b69e6',
},
{
name: 'Key Vault Crypto User',
id: '12338af0-0e69-4776-bea7-57ae8d297424',
},
{
name: 'Key Vault Certificate User',
id: 'db79e9a7-68ee-4b58-9aeb-b90e7c24fcba',
},
{
name: 'Key Vault Reader',
id: '21090545-7ca7-4776-b22c-e363652d74d2',
},
].map(
(r) =>
//Grant the resource roles to the group above.
new azure.authorization.RoleAssignment(
`${vaultName}-${r.id}`,
{
principalType: 'Group',
principalId: vaultReadOnlyGroup.objectId,
roleAssignmentName: r.id,
roleDefinitionId: `/providers/Microsoft.Authorization/roleDefinitions/${r.id}`,
scope: vault.id,
},
{ dependsOn: [vault, vaultReadOnlyGroup] }
)
);
//Write Roles
[
{
name: 'Key Vault Certificates Officer',
id: 'a4417e6f-fecd-4de8-b567-7b0420556985',
},
{
name: 'Key Vault Crypto Officer',
id: '14b46e9e-c2b7-41b4-b07b-48a6ebf60603',
},
{
name: 'Key Vault Secrets Officer',
id: 'b86a8fe4-44ce-4948-aee5-eccb2c155cd7',
},
{
name: 'Key Vault Contributor',
id: 'f25e0fa2-a7c8-4377-a976-54943a77a395',
},
].map(
(r) =>
//Grant the resource roles to the group above.
new azure.authorization.RoleAssignment(
`${vaultName}-${r.id}`,
{
principalType: 'Group',
principalId: vaultWriteGroup.objectId,
roleAssignmentName: r.id,
roleDefinitionId: `/providers/Microsoft.Authorization/roleDefinitions/${r.id}`,
scope: vault.id,
},
{ dependsOn: [vault, vaultWriteGroup] }
)
);
return { vault, vaultReadOnlyGroup, vaultWriteGroup };
};
The Log Module
This module provisions a Log Analytics Workspace, which is used for collecting and analyzing telemetry data from various sources, providing insights into resource utilization and performance.
- Workspace Options:
- immediatePurgeDataOn30Days: which allows data to be purged immediately after 30 days.
- workspaceCapping: Sets a daily data ingestion quota to control costs and manage data volume.
- sku: Defines the pricing tier for the workspace, which affects cost and features.
View code:
import * as azure from '@pulumi/azure-native';
export default (
name: string,
{
rsGroup,
//For demo purpose I config capacity here is 100Mb. Adjust this according to your env.
dailyQuotaGb = 0.1,
sku = azure.operationalinsights.WorkspaceSkuNameEnum.PerGB2018,
}: {
dailyQuotaGb?: number;
rsGroup: azure.resources.ResourceGroup;
sku?: azure.operationalinsights.WorkspaceSkuNameEnum;
}
) =>
new azure.operationalinsights.Workspace(
name,
{
resourceGroupName: rsGroup.name,
features: { immediatePurgeDataOn30Days: true },
workspaceCapping: { dailyQuotaGb },
sku: { name: sku },
},
{ dependsOn: rsGroup }
);
The AppInsight module
This module provisions an Application Insights component for monitoring web applications, linking it to a Log Analytics Workspace for data ingestion.
- AppInsights Options:
- kind and applicationType: Define the type of application being monitored, in this case, a web application.
- retentionInDays: Sets the data retention period to 30 days.
- immediatePurgeDataOn30Days: Allows data to be purged immediately after 30 days.
- ingestionMode: Specifies that data ingestion is done through Log Analytics.
View code:
import * as azure from '@pulumi/azure-native';
export default (
name: string,
{
vault,
rsGroup,
workspace,
}: {
rsGroup: azure.resources.ResourceGroup;
workspace: azure.operationalinsights.Workspace;
vault?: azure.keyvault.Vault;
}
) => {
const appInsight = new azure.insights.Component(
name,
{
resourceGroupName: rsGroup.name,
workspaceResourceId: workspace.id,
kind: 'web',
applicationType: 'web',
retentionInDays: 30,
immediatePurgeDataOn30Days: true,
ingestionMode: azure.insights.IngestionMode.LogAnalytics,
},
{ dependsOn: workspace }
);
if (vault) {
//Add appInsight key to vault
new azure.keyvault.Secret(
`${name}-key`,
{
resourceGroupName: rsGroup.name,
vaultName: vault.name,
secretName: `${name}-key`,
properties: {
value: appInsight.instrumentationKey,
contentType: 'AppInsight',
},
},
{
dependsOn: appInsight,
//The option `retainOnDelete` allows to retain the resources on Azure when deleting pulumi resources.
//In this case the secret will be retained on Key Vault when deleting.
retainOnDelete: true,
}
);
//Add App insight connection string to vault
new azure.keyvault.Secret(
`${name}-conn`,
{
resourceGroupName: rsGroup.name,
vaultName: vault.name,
secretName: `${name}-conn`,
properties: {
value: appInsight.connectionString,
contentType: 'AppInsight',
},
},
{
dependsOn: appInsight,
//The option `retainOnDelete` allows to retain the resources on Azure when deleting pulumi resources.
//In this case the secret will be retained on Key Vault when deleting.
retainOnDelete: true,
}
);
}
return appInsight;
};
The main index.ts module:
This is a main module for the shared project, and a similar structure is maintained across all related projects. This file is tasked with:
- Establishing Resource Groups.
- Deploying all the Azure Resources above.
- Exporting essential resource details for future use by other projects.
View code:
import * as azure from '@pulumi/azure-native';
import * as config from '../config';
import Log from './Log';
import Vault from './Vault';
// Create Shared Resource Group
const rsGroup = new azure.resources.ResourceGroup(config.azGroups.shared);
//The vault to store env secrets env
const vaultInfo = Vault(config.azGroups.shared, {
rsGroup,
//This should be 90 days in PRD.
retentionInDays: 7,
});
//The centralized log workspace and appInsight
const logInfo = Log(config.azGroups.shared, {
rsGroup,
vault: vaultInfo.vault,
});
// Export the information that will be used in the other projects
export default {
rsGroup: { name: rsGroup.name, id: rsGroup.id },
logWorkspace: {
name: logInfo.workspace.name,
id: logInfo.workspace.id,
customerId: logInfo.workspace.customerId,
},
appInsight: {
name: logInfo.appInsight.name,
id: logInfo.appInsight.id,
key: logInfo.appInsight.instrumentationKey,
},
vault: {
name: vaultInfo.vault.name,
id: vaultInfo.vault.id,
readOnlyGroupId: vaultInfo.vaultReadOnlyGroup.id,
writeGroupId: vaultInfo.vaultWriteGroup.id,
},
};
Deployment and Cleanup
Deploying the Stack
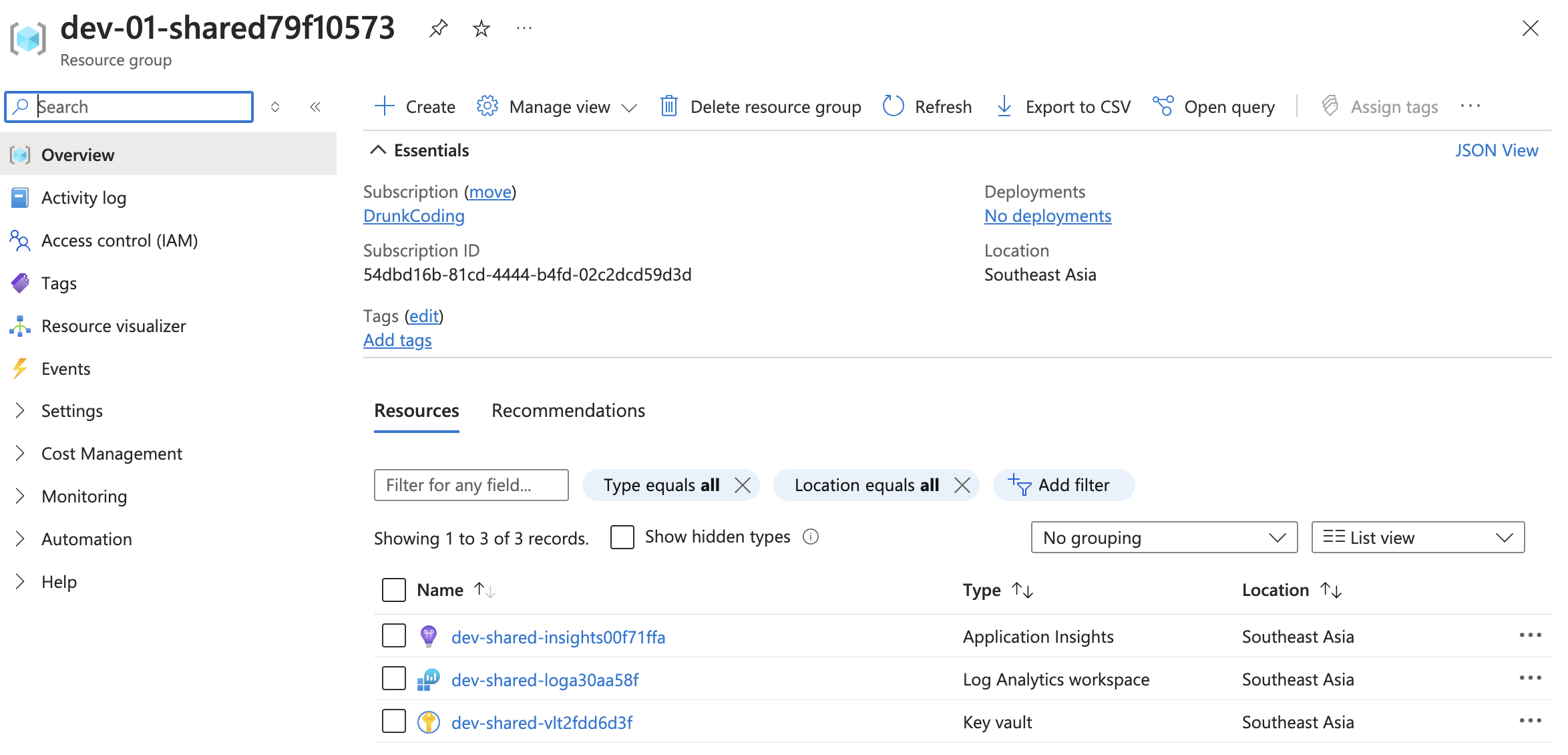
To deploy the stack, execute the pnpm run up command. This provisions the necessary Azure resources. We can verify the deployment as follows:
-
EntraID groups configured for Key Vault access control:

-
Successfully deployed Azure resources:
Cleaning Up the Stack
To remove the stack and clean up all associated Azure resources, run the pnpm run destroy command. This ensures that any resources no longer needed are properly deleted.
Conclusion
By following this guide, we have successfully automated the deployment of secure secret management and centralized log management using Azure Key Vault, Log Analytics, and Application Insights with Pulumi.
This setup ensures that sensitive data is securely stored and that we have real-time monitoring of application performance across our environment.
Implementing RBAC and the principle of least privilege enhances the security posture of our infrastructure. Centralized logging enables us to efficiently troubleshoot issues and gain operational insights.
References
Next
Day 04: Develops a Virtual Network Hub for Private AKS on Azure
In the next article, We’ll walk through the process of developing the first Hub VNet for a private AKS environment using Pulumi. We will demonstrate how to seamlessly integrate a VNet with an Azure Firewall, along with configuring outbound public IP addresses.
Thank You
Thank you for taking the time to read this guide! I hope it has been helpful, feel free to explore further, and happy coding! 🌟✨
Steven | GitHub